This Article for them who have basic knowledge of java but begainer in problem solving. it covered concepts of if-else statement , Array and String manipulation.
At first try your self. you can get help of video tutorial if you failed several time. Solution link given at the bottom of this article.
1. Print the following shapes using loop(s)
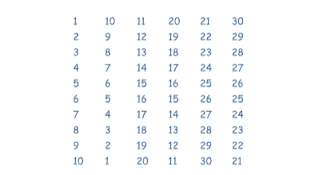
2. Write a program to generate the following output (in the given layout) using
loop(s).
3. Write a program that takes the height and width of a square and print the box of
that height and width with alphabet ‘B’. E.g. if user presses 5 for height and 8 for
width, your program should print the following. (Restrict the user such that
height or width should not be equal to zero).
4. Develop a program that inputs 10 different integers within a while loop and
displays the largest as well as smallest. (Repetition of numbers is not allowed).
5. Write a program that asks the base and exponent (power) from user and print
the result using do while loop. e.g. If base is 2 and exponent is 3, so 2*2*2 is 8.
6. Using for loop, print the result of multiplication of all odd numbers from 1 to 20
and the result of sum of all even numbers from 1 to 100.
7. Print the following shapes using loop(s)
8. Take an integer input from the user, print YES if it is prime number and NO if it
not a prime number. (Prime number is a number which is only divisible by 1 or
itself).
9. using do while print the number of digits this number contains.
10. Take two numbers from the user and print the result of multiplication and
sum of all the numbers between these two numbers. E.g. if user presses 3 and 8
then 4+5+6+7 is 22 and 4*5*6*7 is 840. (Restrict the user such that first
number must be less than the second number).
11. Take an integer input from the user and count all prime numbers from 1 up
to that number, print the total number of prime numbers as well as the largest
one. E.g. if user presses 20, your program should print “Total number of prime
numbers are: 8” (as prime numbers from 1 to 20 are 1, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19)
and “Largest prime number is: 19”.
12. Write a program which asks the user “How many prime numbers you want to
print: “, you have to print that much prime numbers as well as the sum of all
printed prime numbers. If user presses 11, your program should print first eleven
prime numbers, these are 1 3 5 7 11 13 17 19 23 29 31 and sum of these
printed numbers, that is 159. (Restrict the user such that input should not be
negative).
13. Take two integer arrays of 10 indices each and initialize them. Then copy
the contents of both of the arrays in a third array, one consecutive index from
one array at a time.
E.g. if the array1 has 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 stored and array2 has 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 stored then array three will have 1 11 2 12 3 13 4 14 5 15 6 16 7 17 8 18 9 19 10 20 stored.
14. Initialize integer array with 10 random values. Then print the second
smallest as well as second largest element from that array. (E.g. 23 7 2 56 3 8 9.
here second largest is 23 and second smallest is 3). you code might not work for 1 2 2 2 2 5 5 8 8 8 8 8, second largest is 5 and second smallest is 2. You have to
check ur program with many test cases.
15. Declare an array and take input from the user in that array, ask the user to
enter an integer and you have to print index number of that integer. if that
number exists 2 or more time at different indexes then u have to print all indexes
having that integer input.
16. Declare array and take input from the user to fill that array, take two
integer input from the user, you have to find indexes of those numbers and than
exchange those number. if 45 comes at index 3 and 67 comes at index 9. After
exchange, index 3 should contain 67 and index 9 should contain 45.
17. Declare and take input from the user in two arrays a and b, you have to print
all the numbers which exist in both the arrays.
18. Declare and take input from the user in character array, and you have to
print total number of vowels in that array (e.g. d t i o o a r w h s h w q n x b , total number of vowels are 4 (as i o o a ) ).
19. Take two arrays of character type and take input from the user, you have to
exchange the elements of both arrays. array A should contains elements of B, and
B should contain the elements of A.
Credit and Solution Link: https://youtu.be/Sny9Rta3k_Q